Retired Document
Important: This document may not represent best practices for current development. Links to downloads and other resources may no longer be valid.
Key-value observing
Key-value observing is a mechanism that enables an object to be notified directly when a property of another object changes. Key-value observing (or KVO) can be an important factor in the cohesiveness of an application. It is a mode of communication between objects in applications designed in conformance with the Model-View-Controller design pattern. For example, you can use it to synchronize the state of model objects with objects in the view and controller layers. Typically, controller objects observe model objects, and views observe controller objects or model objects.
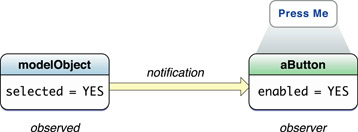
With KVO, one object can observe any properties of another object, including simple attributes, to-one relationships, and to-many relationships. An object can find out what the current and prior values of a property are. Observers of to-many relationships are informed not only about the type of change made, but are told which objects are involved in the change.
As a notification mechanism, key-value observing is similar to the mechanism provided by the NSNotification and NSNotificationCenter classes, but there are significant differences, too. Instead of a central object that broadcasts notifications to all objects that have registered as observers, KVO notifications go directly to observing objects when changes in property values occur.
Implementing KVO
The root class, NSObject, provides a base implementation of key-value observing that you should rarely need to override. Thus all Cocoa objects are inherently capable of key-value observing. To receive KVO notifications for a property, you must do the following things:
You must ensure that the observed class is key-value observing compliant for the property that you want to observe.
KVO compliance requires the class of the observed object to also be KVC compliant and to either allow automatic observer notifications for the property or implement manual key-value observing for the property.
Add an observer of the object whose value can can change. You do this by calling
addObserver:forKeyPath:options:context:. The observer is just another object in your application.In the observer object, implement the method
observeValueForKeyPath:ofObject:change:context:. This method is called when the value of the observed object’s property changes.
KVO Is an Integral Part of Bindings (OS X)
Cocoa bindings is an OS X technology that allows you to keep values in the model and view layers of your application synchronized without having to write a lot of “glue code.” Through an Interface Builder inspector, you can establish a mediated connection between a view’s property and a piece of data, “binding” them such that a change in one is reflected in the other. KVO, along with key-value coding and key-value binding, are technologies that are instrumental to Cocoa bindings.
Copyright © 2018 Apple Inc. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Updated: 2018-04-06